Switching to EV charging isn’t just good for the environment — many government programs offer funding support to reduce your upfront costs.
EV Charging 101
From AC vs DC to charge times and power ratings — we’re here to demystify the world of EV infrastructure. Whether you’re managing a fleet or planning a single install, our in-house experts break it down without the jargon.
kWh (Kilowatt-hour)
The total amount of energy your car’s battery can store. Think of this like the “size of your tank.”
kW (Kilowatt)
How fast your charger can refill the battery — like how quickly petrol flows into a tank.
AC Vs DC
AC charges slower using standard power; DC charges faster by sending power straight to the battery.
Types of Chargers
Slow/Level 1 (2–3kW)
Plug-in to a standard wall socket. Suitable only for occasional or overnight use.
Fast/AC (7kW–22kW)
Wall-mounted or pedestal chargers, common in homes and workplaces.
Rapid/DC (50kW–350kW)
High-powered chargers for short turnaround charging — mostly used in public or depot settings.
Connector Types
Type 2 (AC)
The standard plug for AC charging — used by most modern EVs in Australia.
CCS2 (DC + AC combo)
A combo plug that allows both AC and fast DC charging — now the most common for rapid charging.
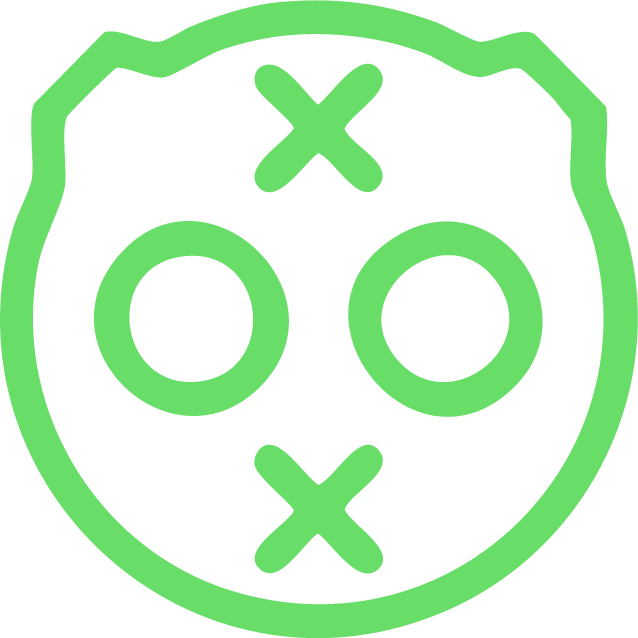

CHAdeMO
An older DC plug type found mostly on older or imported EVs — still supported at many public stations, but becoming less common.

AC Vs DC
AC (Alternating Current): Slower, cost-effective, ideal for long dwell times (e.g., overnight fleet charging).
DC (Direct Current): Faster, more expensive, best for quick turnarounds or high-usage sites.
How to choose?
If your vehicles sit idle for extended periods (like fleets parked overnight), multiple 7kW AC chargers will do the job efficiently.
If your vehicles only have short windows to recharge (like depot-based field teams), one DC charger could rapidly top up the whole fleet.
“How long does it take to charge?” – It depends. Here’s why.
The kW rating of your charger = how much power it can deliver per hour.
Your car’s battery capacity (kWh) ÷ charger output (kW) = approx. charge time from 0–100%.
Example - DC
70kWh battery ÷ 150kW DC = ~30 mins (Assuming your car accepts that rate. Most will automatically throttle to their safe max.)
Example - AC
70kWh battery ÷ 7kW AC charger = 10 hours. But: Even if the charger can deliver 22kW, most cars will only accept 11kW AC.
Battery Health
As the battery nears full charge, the charging rate slows to protect battery health — this is automatic and varies by vehicle.
Grants & Incentives
Switching to EV charging isn’t just a smart environmental move — it’s one that often comes with serious funding support.
Depending on your location and project type, you may be eligible for:
- Rebates for EV charger hardware and installation
- Grants for multi-residential or commercial developments
- Fleet transition support (particularly for councils or logistics providers)
- Charger rebates for EV car dealerships and repairers
- Many programs are first-come, first-served or have limited application rounds
- Most require detailed documentation like site plans, quotes, and project scopes
- Partnering with an experienced installer like Altitude improves your chances of meeting all eligibility and compliance requirements
Yes — we’ve supported clients through numerous successful grant and rebate applications. We’ll advise on what’s currently available, what’s coming soon, and how to best position your project.
In-Focus Projects
A bespoke EV charging solution was delivered for the Volkswagen training facility. The project involved careful assessment of on-site conditions to ensure all minimum requirements were met while integrating seamlessly with existing infrastructure. A combination of AC and DC chargers was installed, supported by a load management system to optimise performance and efficiency. Where possible, existing distribution boards were used, with additional dedicated EV charging distribution boards installed to support future scalability.
A custom EV charging system is currently being delivered for IKEA’s Springvale store, featuring a 300kW DC fast charger and four pedestal-mounted 22kW AC chargers. The installation includes a dedicated 250A EV charging distribution board and full load management to ensure safe, balanced energy usage across the system. The solution is designed to support high-volume usage while maintaining efficiency and scalability in line with IKEA’s sustainability goals.
EV charging infrastructure is being delivered across multiple Milieu residential developments, with 7kW and 22kW chargers installed in resident car bays. Solutions range from full turnkey installations to individual chargers using existing infrastructure. New dedicated EV charging systems are also being installed to support future expansion as EV adoption increases. Each charger is integrated into the site’s OCPP platform, with load management in place to optimise performance. Comprehensive site assessments are conducted to ensure suitability and long-term efficiency of the infrastructure.
This project involved the supply and installation of two 22kW AC chargers for fleet vehicle use in the shared basement of the NDIS facility in Cremorne. The chargers were fully integrated into the base building’s ICN and pre-existing load management system to ensure seamless operation. The team also supported the client with setting up a Chargefox site host account and provided full project management throughout the installation, ensuring a smooth and coordinated delivery.


